Stay Safe: Understanding the WinRAR Vulnerability (CVE-2025-8088)
- gavkoch
- Aug 11, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Oct 3, 2025
As a cybersecurity community, we must remain vigilant against threats that target the tools we trust daily. One of the most urgent of these is a WinRAR vulnerability (CVE-2025-8088) that’s already being actively exploited in the wild. Fortunately, an update is now available to mitigate the threat.
This flaw impacts WinRAR versions prior to 7.13 and leverages a directory traversal bug. Attackers can drop and execute malicious code on a target system without the victim’s knowledge.
How the Exploit Works — Step-by-Step
Crafting the Malicious Archive
Attackers prepare RAR/ZIP files containing payloads with file paths designed to escape the chosen extraction directory. These sequences are crafted to exploit the vulnerability.
Exploitation via Directory Traversal
In vulnerable versions of WinRAR, the software does not properly sanitize extraction paths. This oversight allows files to be written into arbitrary locations, including system startup folders.
Persistence Mechanism
A malicious executable dropped into a startup folder will run automatically on reboot. It uses the current user’s privileges. If that user has admin rights, the system compromise can be significantly more severe.

Delivery Method
Many attacks observed in the wild have used phishing emails with lures such as:
HR Related
Medical Records
Government or banking communications
Post-Exploitation Activities
Installing Remote Access Trojans (RATs)
Stealing browser-stored passwords
Deploying ransomware payloads
Exfiltrating sensitive files
Why This Vulnerability Matters
WinRAR is installed on hundreds of millions of systems. Without automatic updates, old vulnerable versions can persist for years. This makes this exploit a long-term threat if we don’t respond quickly.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
These IOCs are based on samples observed in active campaigns linked to CVE-2025-8088 exploitation. We have included some further information from VirusTotal of the process.
Malicious Files
Adverse_Effect_Medical_Records_2025.rar
- SHA-1: 371A5B8BA86FBCAB80D4E0087D2AA0D8FFDDC70B
- LNK/Agent.AJN, Win64/Agent.GPM

cv_submission.rar
- SHA-1: D43F49E6A586658B5422EDC647075FFD405D6741
- LNK/Agent.AJN, Win64/Agent.GPM
Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (10).rar
- SHA-1: F77DBA76010A9988C9CEB8E420C96AEBC071B889
- Win64/Agent.GMQ
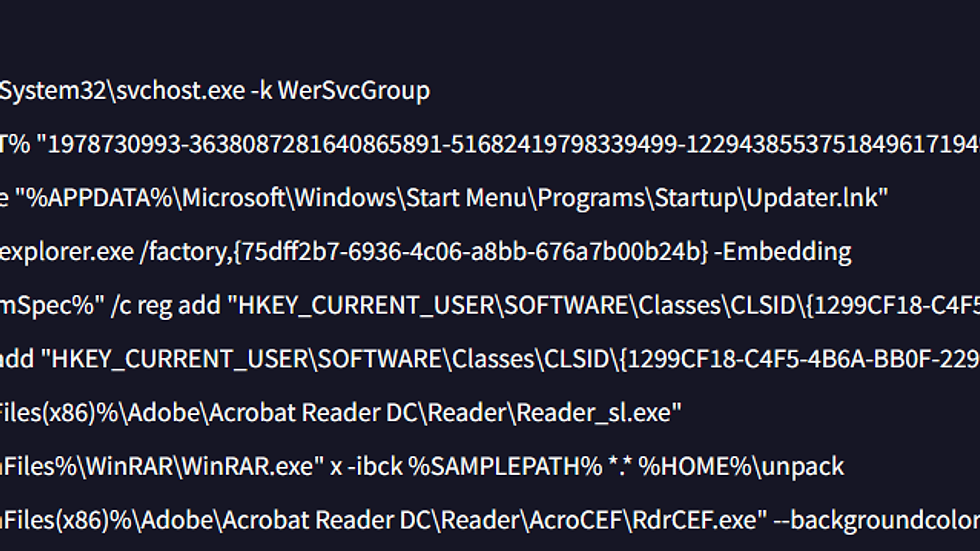
Datos adjuntos sin título 00170.dat
- SHA-1: 676086860055F6591FED303B4799C725F8466CF4
- LNK/Agent.AJN, Win64/Agent.GPM
JobDocs_July2025.rar
- SHA-1: 1F25E062E8E9A4F1792C3EAC6462694410F0F1CA
- LNK/Agent.AJN, Win64/TrojanDownloader.Agent.BZV
Recruitment_Dossier_July_2025.rar
- SHA-1: C94A6BD6EC88385E4E831B208FED2FA6FAED6666
- LNK/Agent.AJN, Win64/TrojanDownloader.Agent.BZV
install_module_x64.dll
- SHA-1: 01D32FE88ECDEA2B934A00805E138034BF85BF83
- Win64/Agent.GNV (MeltingClaw)
msedge.dll
- SHA-1: AE687BEF963CB30A3788E34CC18046F54C41FFBA
- Win64/Agent.GMQ (Mythic agent)
Complaint.exe
- SHA-1: AB79081D0E26EA278D3D45DA247335A545D0512E
- Win64/TrojanDownloader.Agent.BZV (RustyClaw)

ApbxHelper.exe
- SHA-1: 1AEA26A2E2A7711F89D06165E676E11769E2FD68
- Win64/Agent.GPM (SnipBot variant)
Suspicious File Paths
`%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\exe or lnk`
`%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp\exe or lnk`
`%TEMP%\~temp<random>.exe`
C2 Infrastructure
162.19.175[.]44 – gohazeldale[.]com – OVH SAS – MeltingClaw C2
194.36.209[.]127 – srlaptop[.]com – CGI GLOBAL LIMITED – Mythic agent C2
85.158.108[.]62 – melamorri[.]com – HZ-HOSTING-LTD – RustyClaw C2
185.173.235[.]134 – campanole[.]com – FiberXpress BV – SnipBot C2
Further investigation: ESET Research
The threat actor behind RomCom (aka UAT-5647, Storm-0978, Tropical Scorpius, UAC-0180, UNC2596) is suspected to be a Russia-linked cyberespionage group.
How We Can Mitigate the Risk
Here are some practical steps to help mitigate the risk associated with this vulnerability:
| Step | Action | Why It’s Critical |
|------|--------|-------------------|
| 1. Patch Immediately | Install WinRAR 7.13 from the official site. | Removes the vulnerability entirely. |
| 2. Block Suspicious Archives | Email gateway filtering for compressed attachments from unknown sources. | Prevents delivery of exploit packages. |
| 3. Monitor Startup Folders | Audit `%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup` for new files. | Detects persistence early. |
| 4. Use Endpoint Detection | Deploy EDR tools capable of detecting directory traversal exploitation. | Stops payloads before execution. |
| 5. Train Users | Teach teams to verify sender legitimacy before opening archives. | Reduces phishing success rates. |
Our Key Takeaways:
This now patched zero-day is already weaponized, with real-world campaigns underway.
Non-technical users are at highest risk due to phishing delivery methods.
Effective defense requires patching, endpoint monitoring, and phishing resistance training.





Comments